Last updated on 2019-09-30 by Xiang-Jun Lu <xiangjun@x3dna.org>.
The block schematics were created with DSSR and
rendered using PyMOL.
- PDB-id
- 3SSD
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.2 Å)
- Summary
- DNA binding domain of restriction endonuclease bound to DNA
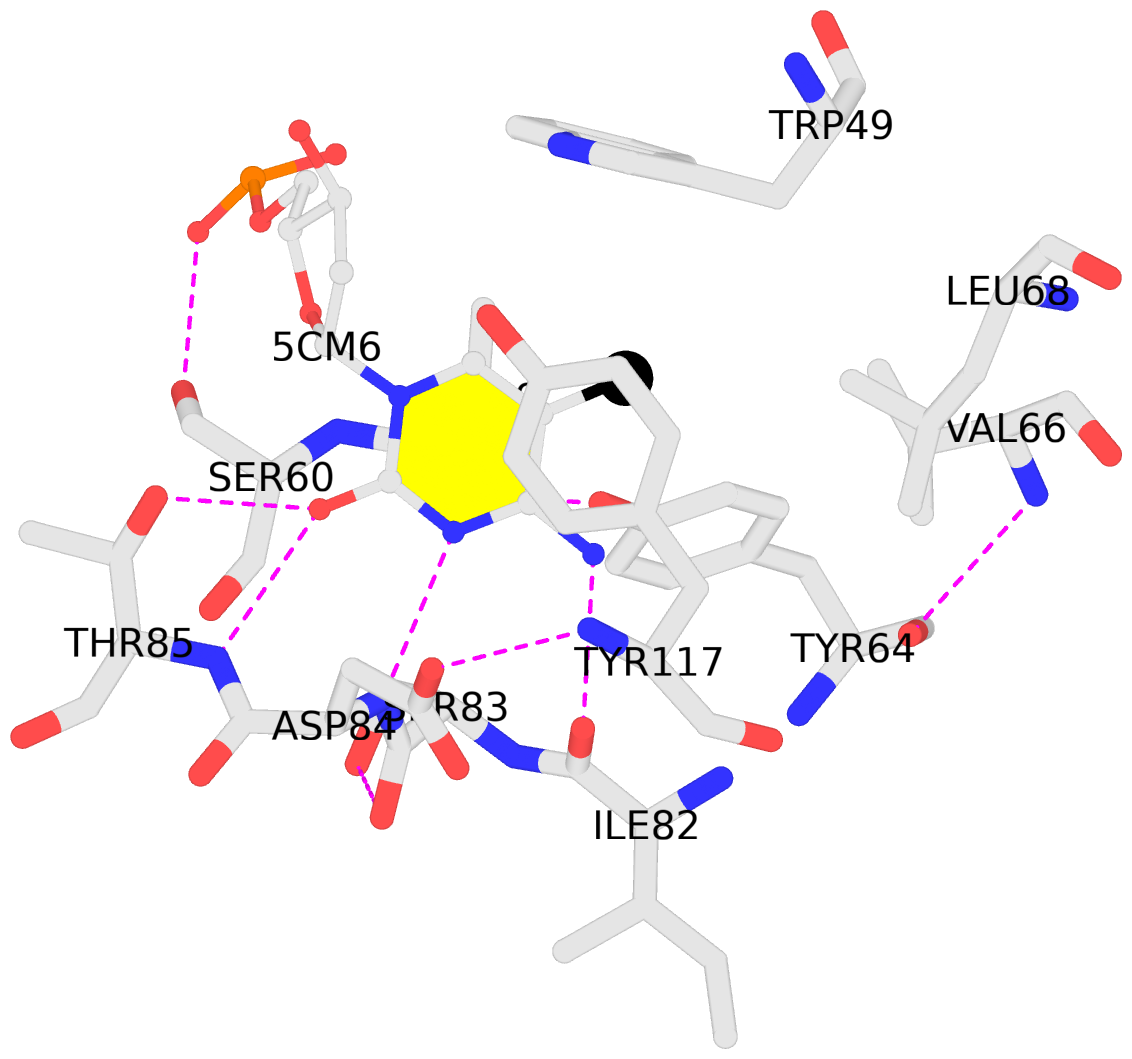
List of 1 5mC-amino acid contact:
-
C.5CM6: stacking-with-B.TYR117 not-WC-paired not-in-duplex
direct SNAP output · DNAproDB 2.0
- Reference
- Sukackaite, R., Grazulis, S., Tamulaitis, G., Siksnys, V.: (2012) "The recognition domain of the methyl-specific endonuclease McrBC flips out 5-methylcytosine." Nucleic Acids Res., 40, 7552-7562.
- Abstract
- DNA cytosine methylation is a widespread epigenetic mark. Biological effects of DNA methylation are mediated by the proteins that preferentially bind to 5-methylcytosine (5mC) in different sequence contexts. Until now two different structural mechanisms have been established for 5mC recognition in eukaryotes; however, it is still unknown how discrimination of the 5mC modification is achieved in prokaryotes. Here we report the crystal structure of the N-terminal DNA-binding domain (McrB-N) of the methyl-specific endonuclease McrBC from Escherichia coli. The McrB-N protein shows a novel DNA-binding fold adapted for 5mC-recognition. In the McrB-N structure in complex with methylated DNA, the 5mC base is flipped out from the DNA duplex and positioned within a binding pocket. Base flipping elegantly explains why McrBC system restricts only T4-even phages impaired in glycosylation [Luria, S.E. and Human, M.L. (1952) A nonhereditary, host-induced variation of bacterial viruses. J. Bacteriol., 64, 557-569]: flipped out 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is accommodated in the binding pocket but there is no room for the glycosylated base. The mechanism for 5mC recognition employed by McrB-N is highly reminiscent of that for eukaryotic SRA domains, despite the differences in their protein folds.
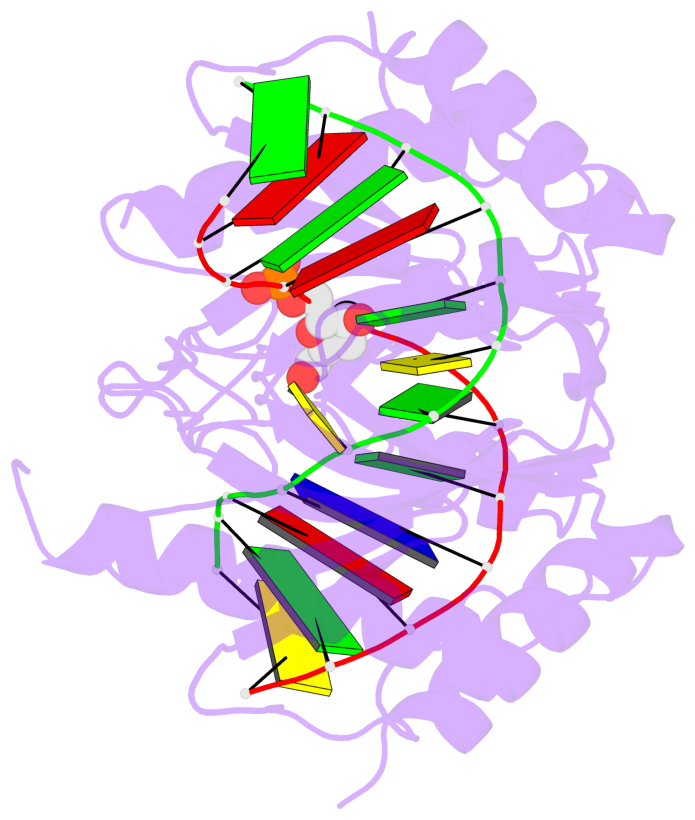
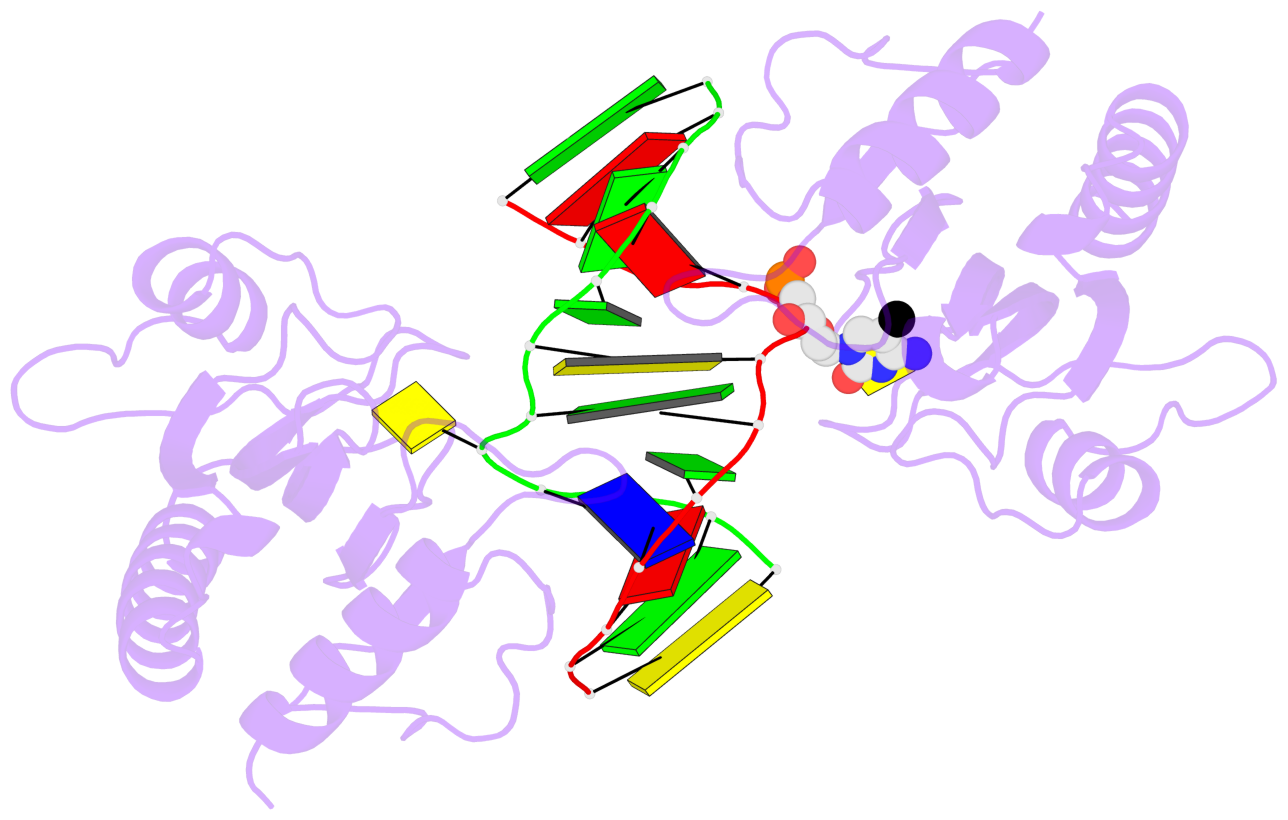
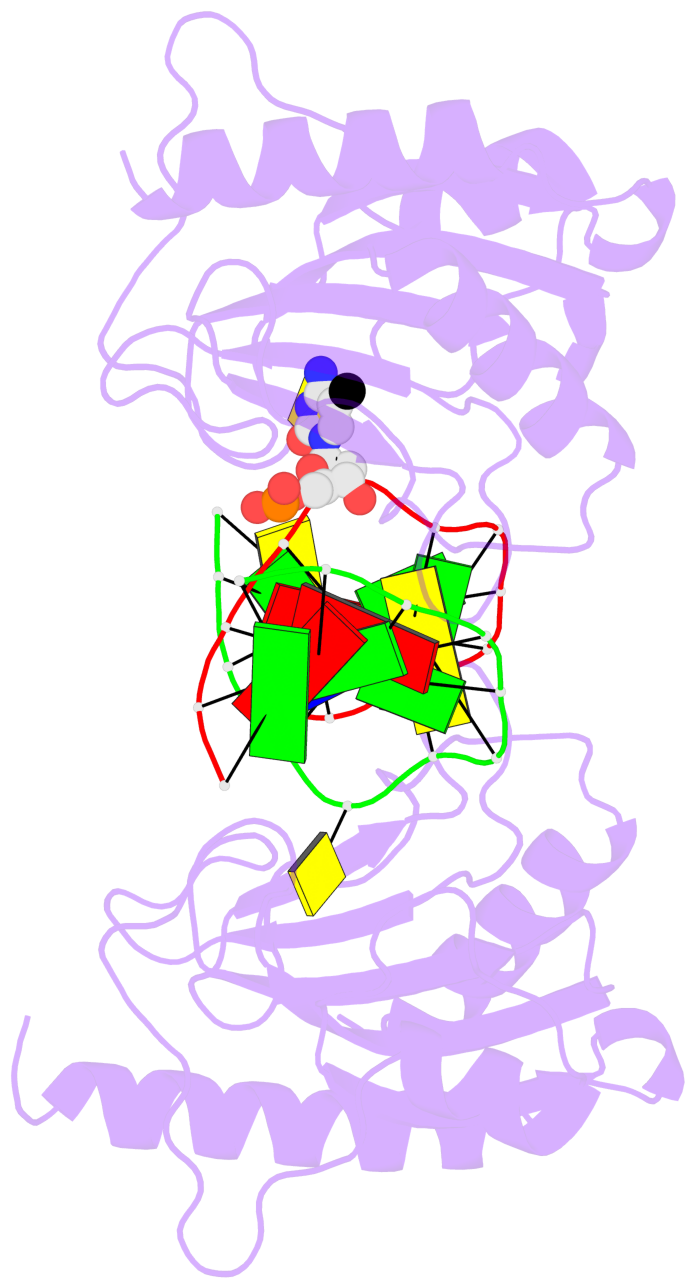
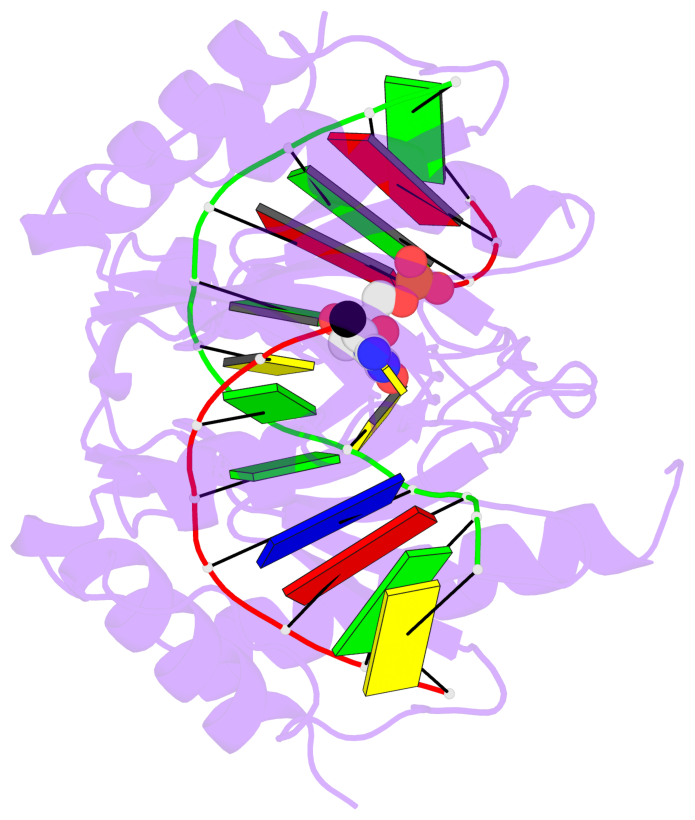
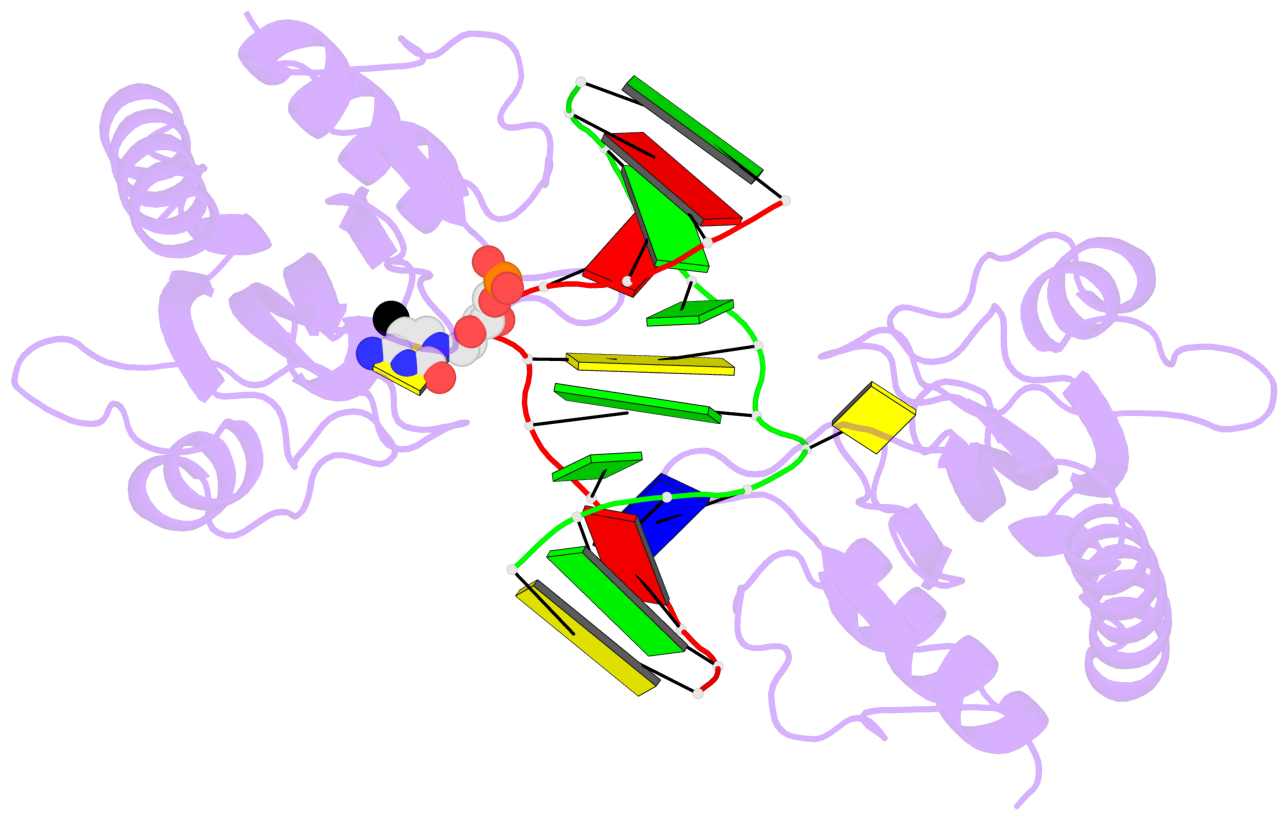
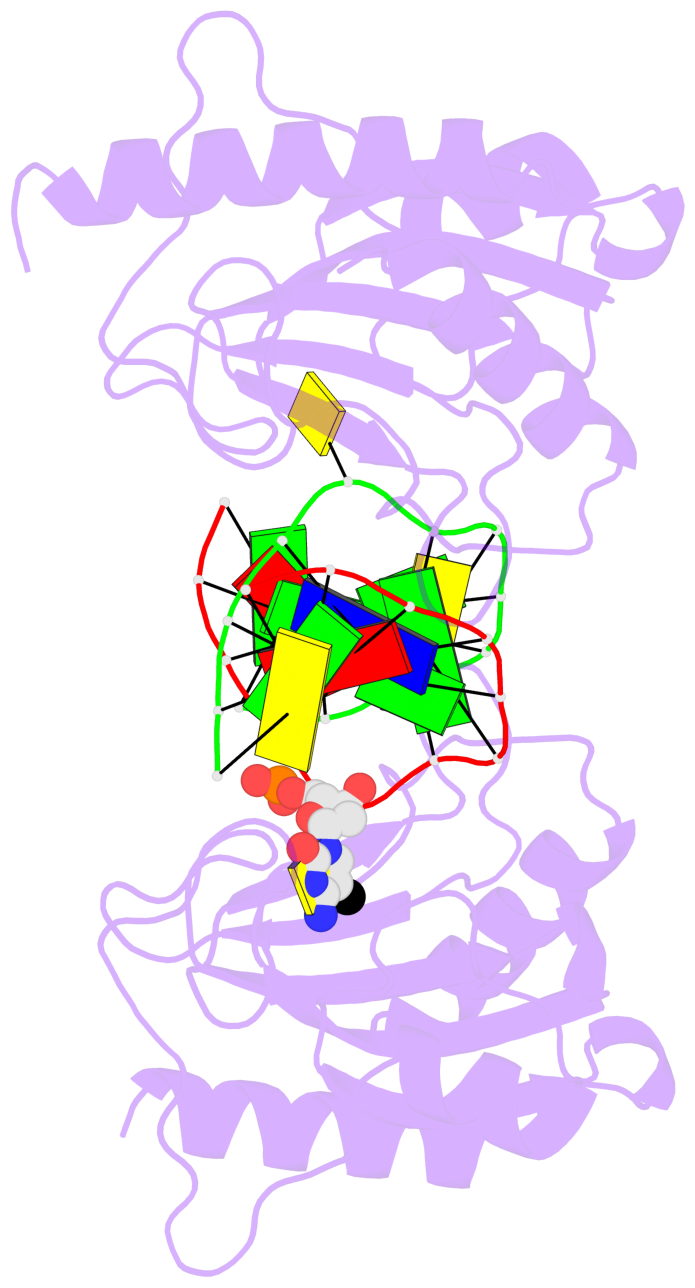
- The 5-methylcytosine group (PDB ligand '5CM') is shown in space-filling model,
with the methyl-carbon atom in black.
- Watson-Crick base pairs are represented as long rectangular blocks with the
minor-groove edge in black. Color code: A-T red, C-G yellow, G-C green, T-A blue.
- Protein is shown as cartoon in purple. DNA backbones are shown ribbon, colored code
by chain identifier.
- The block schematics were created with 3DNA-DSSR,
and images were rendered using PyMOL.
- Download the PyMOL session file corresponding to the top-left
image in the following panel.
- The contacts include paired nucleotides (mostly a G in G-C pairing), and
amino-acids within a 4.5-A distance cutoff to the base atoms of 5mC.
- The structure is oriented in the 'standard' base reference frame of 5mC, allowing for easy comparison
and direct superimposition between entries.
- The black sphere (•) denotes the 5-methyl carbon atom in 5mC.
 |
No. 1 C.5CM6: download PDB file
for the 5mC entry
stacking-with-B.TYR117 not-WC-paired not-in-duplex
|